
it doesn't take much to speak,
silence is the one that take everything away
Hey Aliens (ノ≧∀≦)ノ
it's after CNY holiday
And i'm feeling
sleepy and tired
mostly sleepy
cause i'm still in my holiday mood (──)
BUT assignment is still piling up
and my procrastination ain't helping :|
so i'll force myself into writing this post :V
on this week classes,
we learnt "Interpersonal Relationship"
What is interpersonal Communication ?
from our previous chapterssss~~ (Chapter One ♫ "Foundation Of Human Comm." - 14 Jan 2015)
we learnt that "interpersonal communication"
is about how we commute with another individual (2 person communication)
"a communication between two or more people"
and the key subtopic of this chapters are:
- The Conversation Process
- Principles of Conversation
- Everyday Conversation
- Relationship Stages
- Relationship Theories
- The Dark Side of Interpersonal Relationships
The Conversation Process
The process of conversation started with
Step01 - Opening ; e.g "wuss up" "Hi"
Step02 - Feedforward ; can goes 2 way, (1) new channels of comm. (2)using future msgs
Step03 - Business ; what he or you gonna start talking about
Step04 - Feedback ; responses, E.g "thank bruh"
Step05 - Closing ; E.g "bye" "see you next time"
Principles of Conversation
The principle of Interpersonal Communication are
- Principles of Turn-Taking
- Principles of Dialogue
- Principle of Immediacy
Principles of Turn-Taking
In everyday conversations, there is an active exchange of roles of between speakers and listeners
Also known as the exchanges of cues, or conversational turns (a form of metacommunication/gestures or non-verbal communication).
Both speaker and listener will perform and indicate different and various cues during a conversation process.
With this images of the principle of turn taking (assume created by Mr Anwari himself cause i can't find any online :|)
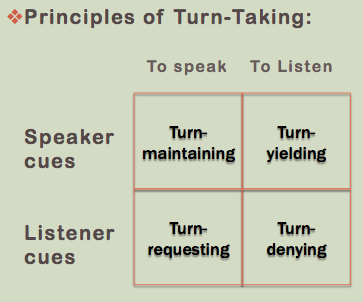
Turn-Maintaining:
Speaker – to speak: His/her role to maintain conversational cues:
Example: Paralanguage, Eye contact
Turn-Yielding:
Speaker – to listen: Indicates they are done talking and wishes to listen.
Example: gestures, verbal
Turn-Requesting:
Listener – to speak: Indicates that he/she is
ready to speak.
Example: Butting in conversation, paralanguage.
Turn-Denying:
Listener – to listen: Indicates that he/she is
not responsive.
Example: Shaking head, looking away…
Speaker – to speak: His/her role to maintain conversational cues:
Example: Paralanguage, Eye contact
Turn-Yielding:
Speaker – to listen: Indicates they are done talking and wishes to listen.
Example: gestures, verbal
Turn-Requesting:
Listener – to speak: Indicates that he/she is
ready to speak.
Example: Butting in conversation, paralanguage.
Turn-Denying:
Listener – to listen: Indicates that he/she is
not responsive.
Example: Shaking head, looking away…
Principles of Dialogue
Dialogue is how two person share their messages to each other.
it is also indicates an interaction rather than just a conversation
the sender and receiver both actively seek to pursue a healthy and meaningful conversation
Principle of Immediacy
Immediacy is the closeness, togetherness between 2 individual (the speaker & the listener)
Giving a unique attention to an individual of interest
Everyday Conversation
Everyday Conversation consist of:
1. Small Talk
2. Excuses and Apologies
3. Complimenting
4. Advice
Although we commute to anyone everyday
there's still a fine line of social etiquette and disastrous communication.
Small Talk
Small talk is a method in which we slowly introduce ourselves into a bigger issue or message
normally considered as a bridge to the conversation (apart from salutations and opening gestures)
Excuses and Apologies
Excuses: Maintain a fair stand on your excuses
We always excuse ourselves and apologize in our everyday conversations,
for the faults that we do, we sometimes defend by giving excuses
and apologize if we are really in the wrong.
Types of excuses:
a. I Didn't do it : ‘No! Really, no!’: Strong declination of your involvement
b. it wasn't so bad : ‘Not my fault’: Mid to neutral stand on your involvement
c. yes, but : ‘I know, BUT..’: Admitting to the fault but still defensive on your involvement
Always maintain an open position
and apologize if you are at fault
Say it like you mean it
Who knows, maybe they will forgive you for your wrong doing ?
..
....
..
Complimenting
Compliment is a “message of praise”
The glue that make relationship stay sticker and hard to pull off.; the interpersonal glue.
2 types of Etiquette of Compliments
Qualified Compliment - praises that really justifies the words; example: someone get a good result in exam.
Unqualified Compliment - praises that is used to just pass on the impression or to mask certain behaviours and intentions; things that you don’t mean to say but said it to get favor or get out of trouble.
Don’t expect favors when you do good.
You may have 2 options when receiving compliments.
>Denial
>Acceptance
For example,
“It’s nice of you to say that, but I know I was terrible” (denial)
“smile and say thank you” (acceptance)
Advice
How do you gives advice?
By experience ? By knowledge?
there are types of advice,
and here's the advice:
#Explore options: Advising others to seek out alternatives.
For example, your friend never have a date before. How would you advice him/her?
#Expert advice/second opinion: Advising others to emphasize or de-emphasize their beliefs and inclinations.
For example, your friend having a persistent cough. How would you advice?
#Delay decision: To delay their decision – wait for others to act, etc.
For example, your friend has two weeks to decide whether to date Girl A or Girl B. How would you advice?
Relationship Stages
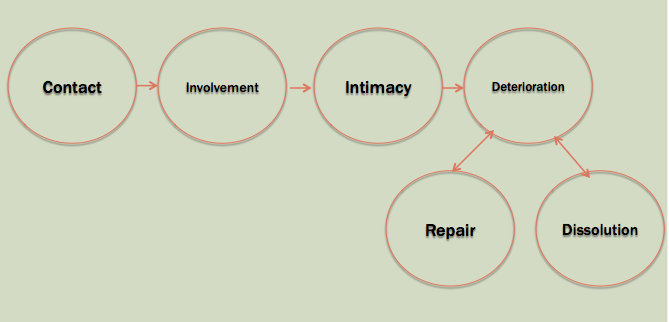
Relationship has stages,
and each stages has it meaning to it
from the above, we can see the steps/stages of relationship
#1 Contact
The first stage of a relationship,
where people become aware of one another's existence, which is impersonal and almost ritualized.
At this stage, perceptual and interactional contact takes place.
Perceptual = human senses (sight, smell, taste, hear, touch)
Interactional = First point of contact; “Hello my name is Ella” and other non-verbal gestures.
For Asians, this is the stage where both (or all) parties are still shy and distance from each other.
(´ . .̫ . `)
While Westerner are more open and try to get close to each other.
(๑・ิ◡・ิ๑)While Westerner are more open and try to get close to each other.
#2 Involvement
Second stage of relationship where people have tighter bonds and engagements with one another
Normally light bonds of friendship and being added into the social circle.
At this stage, both testing and intensifying stages take place.
Testing stage = “Hey, do you want to come out for a drink?”; “Do you like this song?”; “Are you a Manchester United fan as well?”
Intensifying stage = The amount of times or commitments you committed to one another – appointments, dating, etc.
#3 Intimacy
Third stage of relationship where people have a deep and committed relationship with one another
Relationships grow stronger, explicit displays of affection, communication and bond with one another.
At this stage, interpersonal commitment and social bonding will take place.
Basically at this stage, you've become familiar and comfortable with each other.
Naturally, people with the same likings, beliefs and ideas will group with one another and form ‘clicks’ or groups.
#4 Deterioration
Fourth stage of relationship where other communication factors such as temporal, cultural or societal context weakens the bond with one another.
At this stage, both intrapersonal and interpersonal dissatisfactions become apparent.
Reality hurts: At some stage, everybody grows up.
You would be considered lucky if you are still close to your childhood friends when you are an adult
Often we see and experience changes with people and even ourselves in our lives due to different stages of life (youth, young adult, adults, etc.) that has different priorities.
#5 Repair
Fifth stage of relationship where those affected in the deterioration stage try to work things out with one another.
At this stage, intrapersonal and interpersonal repairs take place.
Intrapersonal – you may consider changing your behaviors or perhaps changing your expectations of your partner.
Interpersonal – you talk and discuss about the problems.
#6 Dissolution
Sixth and last stage of relationship where bonds are broken or returned back to a platonic (before friendship or neutral level).
At this stage, interpersonal and social separation takes place.
For example, you separate yourself from the person you don’t like or have differences with, or you separate yourself from the group that you hang out with because you don’t agree with their lifestyle.
Interpersonal separation – you may not see each other anymore or may not return messages, move into separate apartments, etc.
Social or public separation – avoidance of each other and a return to being “single” (divorce, etc).
Relationship Theories
The list of Relationship Theories:
1. Attraction Theory
2. Relationship Rules Theory
3. Relationship Dialectics Theory
4. Social Penetration Theory
5. Social Exchange Theory
6. Equity Theory
@Attraction Theory
Consist of:
a. Similarity: Attraction to individuals with similar taste, beliefs, ideas with you
b. Proximity: Attraction to individuals who are close to you in terms of range and location
c. Reinforcement: Attraction to individuals who reinforces your personality and lifestyle
d. Physical Attractiveness and Personality: Attraction to physical and mental attributes; inner and outer beauty.
@Relationship Rules Theory
Different relationships have different relationship levels and attributes.
a. Friendship Rules
Acquaintances, Normal Friends, Best Friends…
There are rules with each category and we must respect the rules and boundaries
b. Romantic Rules
Similar to friendship rules but more towards lovers and couples.
Varies with different cultural practices
Examples:
Westerners are more direct in public display of affection (PDA)
while Asians are more conservative
c. Family Rules
Different roles in the family setting would impact relationships within and outside of the family.
For example: Traditional Family Setting
The Father is the figurehead of the family and have the utmost authority.
Similarly brothers and sisters also have rules to abide to with each other
the elder sibling would have the authority over the younger sibling.
d. Workplace Rules
Different roles in the workplace would also impact relationship forming and interpersonal communication.
For example: Superiors will act in a certain way to their peers and to those below them
likewise, executives will act in a certain way towards their peers and to those above them.
@Relationship Dialectics Theory
People in relationships often want to explore the extremes of opposite qualities.
Three pairs of opposites are: -
> Closedness and openness:
Individuals like the exclusive attention of one another yet at the same time they like to be involved in a society or group.
>Autonomy and Connection:
Individuals like to have both independency and dependency on one another.
For example: Girls asking guys’ opinion – girls actually know what they want already and they actually do not need the guy to tell them what to do but they still want to hear it.
>Novelty and Predictability:
Individuals like surprises or uniqueness as well as sustainable and predictable things or routines
and schedules (which is why some are high ambiguity and some have low ambiguity)
@Social Penetration Theory
People in relationships (not only lovers, but friends included)
often have the need to explore each other’s personalities.
Deeper relationships would go deeper into the core personality of the person.
Table of social penetration:
The more you know the person, the deeper the level of conversation and the more meaningful it becomes = depth of relationship.
Similarly, the more you know the person, there are more things you can talk about with the person = breadth of relationship.
Both these theories suggests that individuals form relationships with one another based on whether or not it would bring benefit to them
Example, improving their own network or circle of friends,
increasing their chances of getting a job in the company,
or simply making them more popular and well-received.
@Equity Theory (Rewards = Costs)
Equity Theory is more towards forming professional relationships with one another
Example, forming a working partnership with someone else,
where if you put in a certain amount of money into the company,
you would expect the other person to do the same.
If you do more work,
you would expect the get more of the profit than your partner who did less work.
The Dark side of Interpersonal Relationship
Relationships can get complicated and can lead to ugly things in life and with one another.
One of the most common example is jealousy, due to a human nature called envy.
Different types of jealous can occur:
a. Cognitive jealousy - Suspicious thinking, worrying and exaggeration of things that you think would occur.
b. Emotional jealousy - Seeing someone you like react to something else that is out of your control or reach.
c. Behavioral jealousy - Responses or behavioral changes that takes place with the individual as a result of the envy and jealousy.
If the above problem or anti social behavioural is not fixed,
relationship violence will occur.
Such as, Physical abuse , Verbal or emotional abuse – especially through social media (Facebook, Twitter), Sexual abuse
see you guys next time :DDD
No comments:
Post a Comment